Welcome to our “Beginner’s Guide to Web 3.0: What is Web3?” In this comprehensive guide, we aim to demystify the complex world of Web3. We’ll delve into the origins of Web3, its key principles and how it contrasts with Web2 and Web1 eras. Exploring what the future might look like in a world powered by Web3, including the potential benefits and risks.
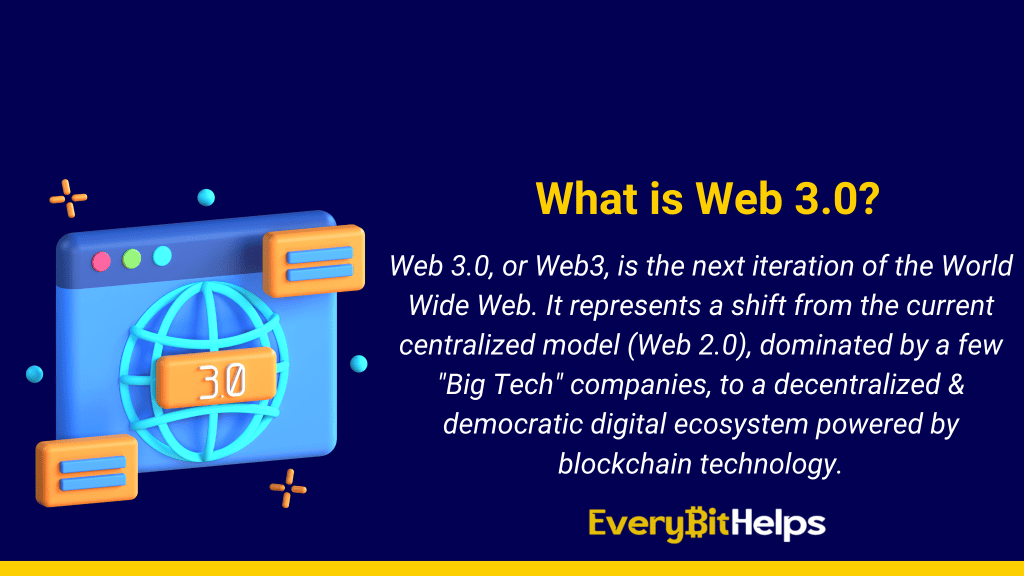
Web 3.0, or as it’s more commonly known, Web3, is the next iteration of the World Wide Web. It represents a shift from the current centralized model (Web 2.0), dominated by a few “Big Tech” companies, to a decentralized and democratic digital ecosystem powered by blockchain technology.
So, let’s dive into this beginner’s guide to Web3 to help you better understand the future of the internet and how it might affect you.
Beginner’s Guide to Web3: Web 3.0 Explained

What was Web1? (1990-2004)
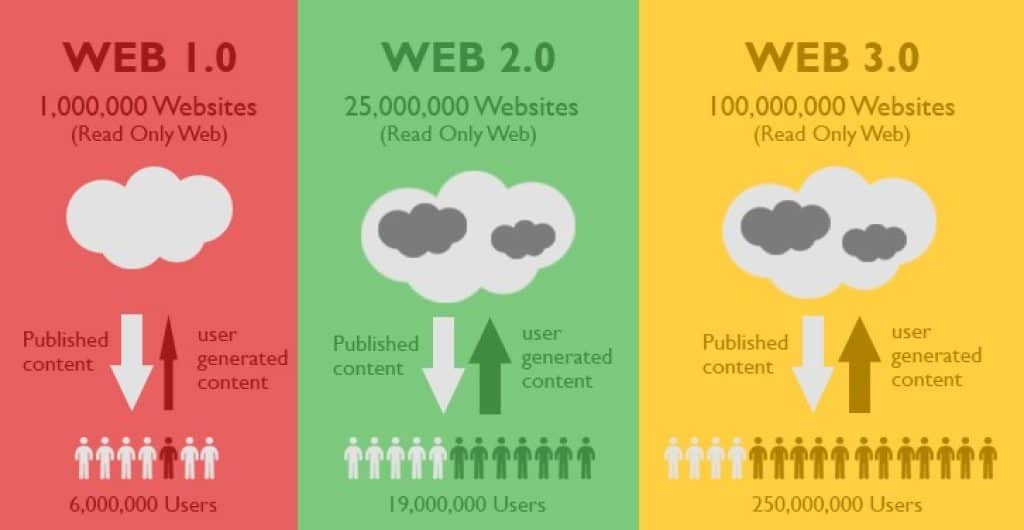
The inception of the digital era began with Web 1.0 in the 1990s, marking the first significant strides in the web’s evolution. This stage of the web, often dubbed the “Read-Only” era, presented the internet as a space where information could be consumed, but the interaction was limited.
Web1 was defined by static, read-only pages where users had little to no opportunity to influence or interact with the content they were viewing. The information that had once been bound to newspapers and library shelves was now becoming accessible online. These static web pages served as digital libraries where users could glean information from a wider array of sources than ever before. However, the functionality was limited despite the vast amounts of data available.
The primary mode of communication during the Web1 era was through emails, a groundbreaking feature at the time. This presented a whole new level of connectivity, but the ability for users to generate their own content was virtually non-existent. Websites were primarily text-based, limited in multimedia content, and user participation was largely confined to reading information rather than creating or influencing it.
Despite these limitations, Web1 set the stage for future advancements. It marked the beginning of the digital age, converting physical information into digital format and making it globally accessible. While it might seem primitive by today’s standards, it was a crucial first step in the journey that has led us from the static, one-sided internet of Web1 to the dynamic, interactive Web2, and now towards the decentralized promise of Web3.
What is Web2? Read-Write (2004-now)
Emerging around 2004/2005, Web 2.0, also known as the “social web,” marked a significant evolution in the internet’s journey. For the first time, users could consume content and generate it, fostering a lively, interactive digital landscape. This interaction was made possible by technological advancements like JavaScript, HTML5, and CSS 3, which allowed websites to evolve from static pages to dynamic, interactive platforms.
Web 2.0 turned the internet into a “Read/Write” space, granting every user the power of content creation and interaction. Users could express their interests, share opinions, interact with others’ content, and even influence the type of content produced by news agencies, media outlets, and creators.
However, the democratization of content creation under Web 2.0 came with a price: the centralization of power. As tech companies like Facebook grew, the balance of power shifted from individual users to these corporate giants. Under the pretence of enhancing user experience, these companies began collecting vast amounts of personal data, often only to sell it to advertisers. In effect, users became the product, their data a commodity for companies to profit from.
Instances of seeing an ad for a coffee place on your Facebook newsfeed after a chat about the best coffee spots are all too common. These occurrences illustrate how our activities are constantly monitored and our data utilized. Privacy on the web became increasingly elusive, even when using features like Incognito mode.
However, these tech giants’ control is not limited to data collection. They can control user access, banning or limiting accounts if they deem users to be violating their terms of use. They can also curate what content users see, shaping the digital landscape according to their perspectives and interests.
While Web 2.0 propelled the development of the web to new heights, it also led to an unprecedented consolidation of control. This centralization has left a handful of entities with the power to make far-reaching decisions on behalf of the users, raising questions about privacy, data security, and freedom on the internet.
What is Web3? Read-Write-Own
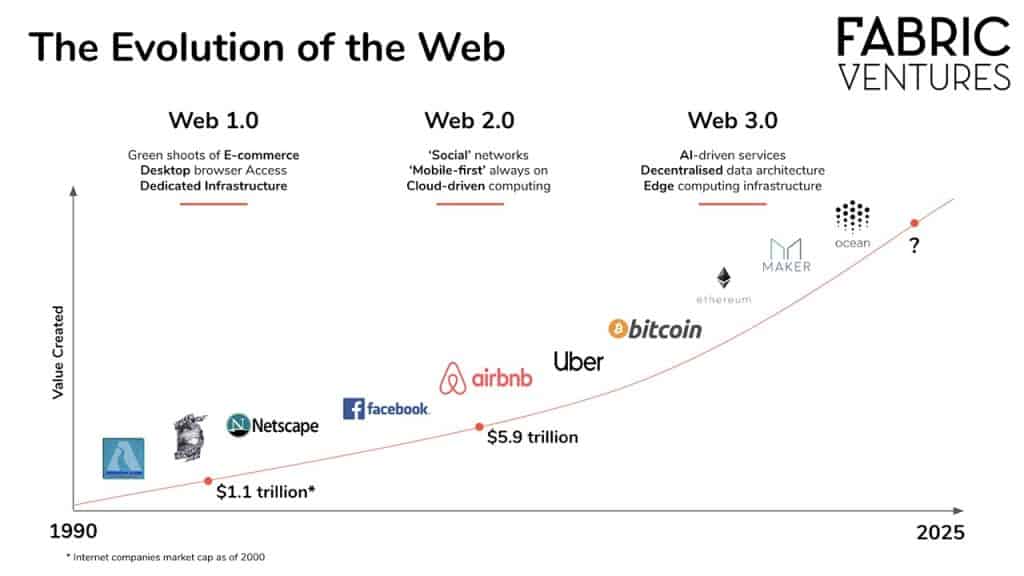
Web3, also known as Web 3.0, represents the next generation of the internet. This concept integrates the principles of decentralization, blockchain technology, and token-based economics into the World Wide Web.
In contrast to Web 2.0, where data and content are mostly centralized in a handful of large technology companies (also known as “Big Tech”), Web3 aims to distribute control across the network. The term “Web3” was initially coined by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood and has gained significant attention from cryptocurrency enthusiasts, technology companies, and venture capital firms since 2021.
Web3 envisions an internet where users have a financial stake and more control over their web communities. It includes applications in cryptocurrencies, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and decentralized finance (DeFi).
However, it is important to note that while Web3 offers potential solutions to privacy, centralization, and financial exclusion concerns, it also presents new challenges and risks. These include questions about data security, scalability, the potential for fraud, and the environmental impact of blockchain technologies. Critics also debate its potential to influence the power dynamics of the internet, both positively and negatively.
Overall, Web3 is anticipated to transform the online experience as dramatically as personal computers and smartphones did, marking a significant shift in how we interact with digital platforms.
Web3 Features
Web3 elevates the user experience to unprecedented levels of control and ownership. It marks an evolution towards a more democratic digital space where users consume and contributes content and exercises absolute ownership over their online assets and data.
So, let’s delve deeper into the intricate workings of Web 3.0 and explore its groundbreaking features and unique capabilities. We aim to provide you with an understanding of how Web 3.0 is redefining the Internet’s landscape and carving a path for a more egalitarian, user-centric digital future.
Users Become Decision Makers
Web3 empowers you to become more than a consumer or contributor; it allows you to be a decision-maker, controlling how you interact with the web. Instead of corporations dictating the use of your data, you decide its fate. If you opt to have your data sold to advertisers, fair compensation will be your right, not a courtesy. You can also choose to experience an ad-free web, keeping your data exclusive to you.
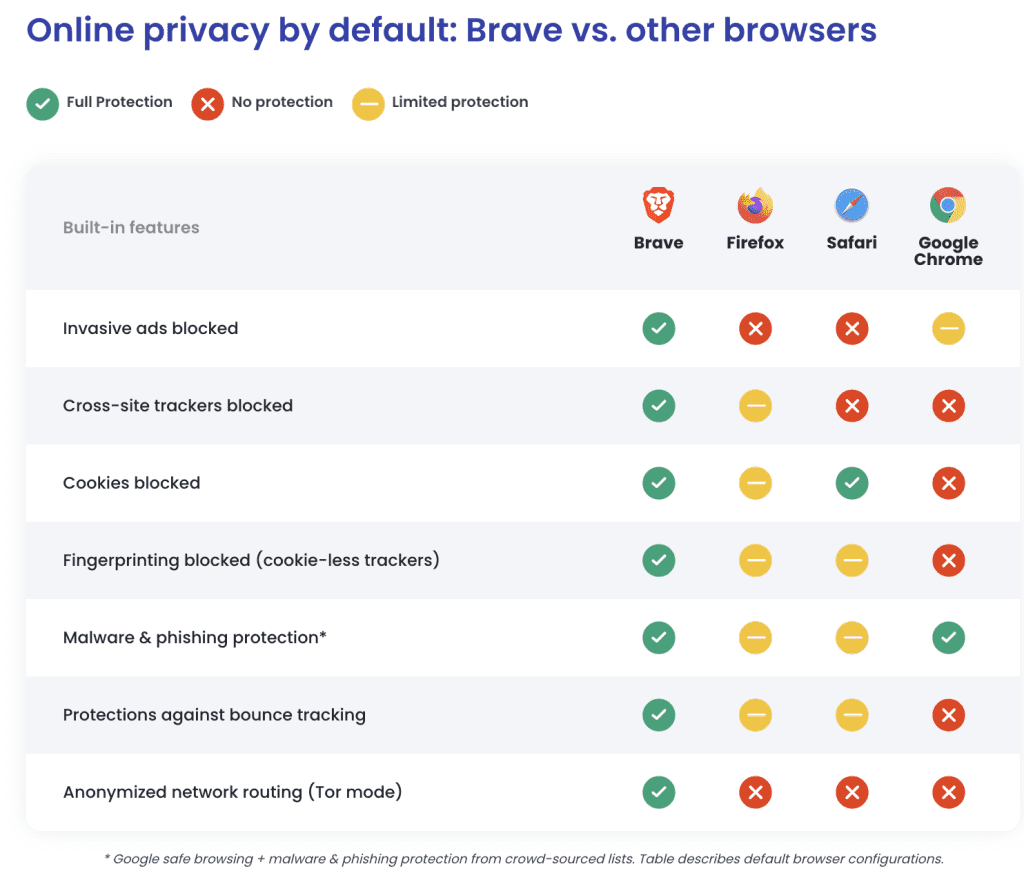
An existing example is the Brave Browser, which rewards users with its native crypto token BAT for opting to view ads.
Unleashing the Power of Permissionless
Web3 eliminates gatekeeping, embodying a permissionless environment. This means you can access any decentralized application on the internet using just your wallet, which requires nothing more than a functional email address to set up.
Decentralizing Authority
Web3 promotes a web ecosystem where no central authority can unjustly revoke your access. Furthermore, it empowers you to take part in the governance of your platforms. Community members can contribute to decision-making processes by utilizing decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) and protocol-specific governance tokens, creating a democratic environment where decisions are made collectively.
Leveraging Web3 Tools
In the Web 3.0 era, tools like NFTs, blockchains, and cryptocurrencies have become instrumental in restoring control of your web experience by eliminating middlemen. For instance, NFTs allow you to retain greater control of your digital assets, such as artwork, music, and tickets.
Eliminating a Central Point of Failure
Another distinctive feature of Web3 is its robustness, achieved by eradicating a central point of failure. In contrast to Web2 systems, where a single server’s failure can disable an entire platform, Web 3s decentralized architecture ensures continued operation even if a node goes down. Your data is distributed across multiple nodes, protecting the system against network outages and security breaches.
Whenever you go on YouTube to watch a video, you send a data request to a central server on YouTube, which stores all videos. Once the central server receives your request, it will find that video from its storage and play it for you on its website. If this central server goes down, you will not be able to access YouTube, and if it gets hacked, all the data stored on the server will get into malicious hands.
This happened in October 2021 when Facebook’s central server went down and was unavailable for 6 hours, and the world came to a standstill. With a central source, there is a greater chance of network outage or failure.
With decentralization in Web3, data is distributed across several servers (or nodes), and there is no single point of failure. If one node is hacked or goes down, the system keeps functioning.
Embracing Continuous Improvement
Web3 thrives on evolution and improvement. The code underpinning applications is open-source, allowing anyone to view it. Developers and tech enthusiasts can take this code, tweak it, and build improved versions, fostering a dynamic environment of continuous enhancement.
Interoperability
Interoperability is another key feature to consider. This refers to the ability of different systems and applications to work together, exchanging and using information. Web 3.0 promotes seamless interaction between different platforms and applications, creating a more connected and efficient Internet ecosystem.
Privacy and Security
Lastly, Web 3.0 places a heightened emphasis on privacy and security. Using cryptographic techniques and decentralized storage, Web 3.0 gives users enhanced control over their personal data and protects against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Examples of Web3
Web3 is currently a work in progress, but its main principle is to establish a decentralized internet experience not dominated by corporations or governments. This evolution seeks to give users more control over their online experience and data, with a backbone largely powered by blockchain technology.

Some examples or use cases of Web 3.0 technologies:
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. They operate decentralised, eliminating the need for intermediaries and making transactions transparent and efficient.
- Automated Content Creation: Powered by AI and Machine Learning, automated content creation is an exciting possibility in the Web3 era. This technology can be leveraged to generate content dynamically, offering personalized user experiences.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): DAOs are member-owned communities without a centralized authority, run by programming code and a collection of smart contracts written on the blockchain.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Unique digital assets representing ownership of a specific item or piece of content, NFTs are an emerging application within the decentralized finance (DeFi) space.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): refers to the shift from traditional, centralized financial systems to peer-to-peer finance enabled by decentralized technologies built on Ethereum and other blockchains.
- Metaverse: Envisioned as an interactive virtual space where users can interact with a computer-generated environment and other users, the Metaverse is expected to be a prominent feature of Web3.
These are just a few examples of the various possibilities and applications. Web3 can offer. It is essential to note that while Web 3.0 offers exciting opportunities, it also comes with potential risks and challenges that need to be carefully considered and managed.
Web3 Careers: What is the Future of Web3 Jobs?
The rise of Web3 and AI, centring around decentralized networks and applications using blockchain technology, creates a new wave of job opportunities. Just as Web2 brought in jobs like app developer, social media manager, and SEO specialist. Web3 is likely to create new roles we’re only beginning to understand.
We have put together some examples of Web3 careers:
- Blockchain Developer: Blockchain developers will be critical in building the decentralized applications (dApps) that form the backbone of the Web3 ecosystem. This role would be akin to app developers in the Web2 era.
- Smart Contract Engineer: These professionals will design and implement smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Analyst: Just like financial analysts in the traditional finance sector, DeFi analysts will help companies make sense of the financial systems and investment opportunities in the DeFi space.
- Blockchain Legal Consultant: As the blockchain industry grows, so does the need for legal expertise in this area. Legal consultants specializing in blockchain can advise on regulatory compliance, intellectual property rights, and more.
- Blockchain Data Analyst: With vast amounts of data being generated by blockchain transactions, professionals who can analyze and interpret this data will be in high demand.
- Metaverse Architect: With the advent of the Metaverse, experts who can build and design in these virtual, often blockchain-based, spaces will be essential.
- AI Ethicist: As AI is increasingly incorporated into decentralized systems, specialists will need to understand the ethical implications of these technologies and ensure they are used responsibly.
- Decentralized Machine Learning Engineer: Like machine learning engineers today, these engineers will focus on creating and deploying machine learning models in decentralized networks, potentially using decentralized data.
- Quantum Computing Expert: Quantum computing has the potential to disrupt both AI and blockchain technology. Experts who can work at the intersection of these fields will be crucial.
- Data Privacy Specialist: Given the importance of data in AI and the transparency of blockchain, professionals who can navigate these waters to ensure user privacy will be critical.
How to Invest in Web3?
Investing in Web3 and the future of the Internet involves understanding and navigating the intersection of various emerging technologies, including blockchain, cryptocurrency, decentralized finance (DeFi), and more.
- Understand What Web3 Is: Web3, or Web 3.0, represents the next phase of the internet’s evolution. Web3 promises a decentralized, permissionless internet that returns data control to the users. This is primarily achieved through blockchain technology. Users will fully own their content, data, and assets via blockchains.
- Identify Your Interest: As an investor, it’s crucial to determine what aspect of Web3 interests you most. Are you more intrigued by blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies? Or are you more drawn to technologies like decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs)? Understanding your interests will help guide your research and investment decisions.
- Choose Your Investment Method: There are various ways to invest in Web3, including stocks in companies that are driving the Web3 movement, cryptocurrencies that underpin the Web3 ecosystem, and NFTs that represent unique digital assets on the blockchain. You could also consider angel investing or buying into a crypto company’s Initial DEX Offering (IDO) or Initial Coin Offering (ICO). This involves investing in a company by participating in a seed round or buying its coin before its official launch.
- Conduct Thorough Research: Just like any form of investment, investing in Web3 carries risks, so it’s essential to do adequate research and have a good investment strategy. Beware of investment narratives. While many Web3 projects have compelling stories and visions, looking beyond the hype and understanding the project’s fundamentals3 is crucial.
- Consult with Professionals: Given the complexity and rapidly evolving nature of the Web3 space, consulting with professionals or financial advisors who understand the industry can be beneficial. This might include venture capital firms that have a focus on Web3 investments.
While Web3 offers promising opportunities, it’s also a relatively new and unregulated field, making it riskier than traditional investments. Always be sure to do your due diligence and never invest more than you’re willing to lose.
Conclusion: What is the Future of Web3?
As you can see, there is a lot of value to Web 3.0, which will change how we live and interact digitally. It is just starting out, so we should see massive improvements in the tools and technologies in the coming years. All in all, helping us take back control from the world’s major companies and allows us to use the internet on our own terms.
As we look to the future, Web3 represents a profound shift in how we interact with the internet and digital technologies. It aims to reshape the online landscape, emphasising decentralization, transparency, and user ownership and control.
Web3 technology brings forth a vision of the internet where individuals are not just consumers but also contributors and owners. The rise of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, NFTs, DeFi, and DAOs showcases a future where everyone can participate in digital economies directly, without intermediaries. This starkly contrasts the current Web2 model, where a few tech giants control and profit from users’ data.
A more decentralized internet will profoundly impact various sectors, from finance to social media, healthcare, and more. The introduction of smart contracts, for instance, could revolutionize how we form agreements, creating automated, self-enforcing contracts that can reduce costs and friction.
In the future, we may see more Web3-based platforms and applications and the rise of new careers focused on blockchain, crypto, and other Web3 technologies. As more people learn about and invest in Web3, we can expect increased demand for these skill sets.
However, the future of Web3 is not without challenges. Regulatory hurdles, scalability issues, energy consumption concerns, and the need for user-friendly interfaces are among the obstacles that must be addressed as we move towards a more decentralized internet.
FAQs
When did Web3 start?
Web3 doesn’t have a definitive starting point in time. Instead, its conception and growth represent an evolutionary process built upon the foundations of its predecessors Web 1.0 and Web 2.0. The concept of Web 3.0 was first introduced around 2006, but the journey towards its full realization has been gradual and is still in progress.
A significant marker in the timeline of Web 3.0 was the advent of blockchain technology, starting around 2009 with the launch of Bitcoin. This disruptive technology underpins the idea of a decentralized web, a core aspect of Web 3.0, where users regain control over their data.
Another pivotal moment in the progression of Web3 occurred with the introduction of Ethereum in 2015. Ethereum introduced the concept of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts, elements intrinsic to the Web 3.0 ethos.
Web 3.0, in essence, represents the next evolution of the internet, deeply intertwined with blockchain technology.