In this beginner’s guide to password security, we will look at what Lowercase and Uppercase passwords are. Plus, what is the best way to create and store your online passwords?
Every website that collects your personal information requires users to create a secure online password to protect their data and content. The password is used for authentication and access control. The more complex your password is to guess, the better it is in terms of security.
Unfortunately, creating and remembering online passwords can be a real pain. Over time, we can get into bad habits and start reusing and creating passwords using our personal or close family names, date of birth, etc.
This is why many websites require using lowercase and uppercase letters when creating a password. Some websites must use numbers, special characters, and other authentication methods.
Let’s learn more about lowercase and uppercase passwords and how they affect online security.
What is a Password?
A password is a distinct and secure combination of characters designed to verify a user’s identity during authentication. It acts as a digital key, similar to how a physical key unlocks a door, enabling access to a device, application, or website in conjunction with a username. Passwords can be composed of an intricate mix of letters, numbers, and special symbols, enhancing their security.
When constructed of multiple words, this security measure is often called a “passphrase,” providing an extended layer of protection through its increased length and complexity. In contrast, when a password is composed solely of numbers, it is typically known as a “passcode” or “passkey,” akin to Personal Identification Numbers (PINs) used in banking and secure access systems. These variations cater to different levels of security needs and user preferences.
What is a Lowercase Password?
A lowercase password is a type of password that consists entirely of lowercase letters. This means it does not include any uppercase letters, numbers, or special characters. For example, a password like “applepie” is a lowercase password.
While lowercase passwords can be easier to remember and type, especially on mobile devices, they are generally considered less secure than passwords that include a mix of character types. This is because the number of possible combinations is significantly lower when only lowercase letters are used, making such passwords more vulnerable to brute-force attacks, where an attacker tries every possible combination to guess the password.
Here are some examples of lowercase passwords:
- monica
- joshuagreg
- peterphilip
- alexandriab
What is an Uppercase Password?
An uppercase password is a password that consists entirely of uppercase letters, meaning it does not include any lowercase letters, numbers, or special characters. For instance, a password like “GREATDAY” would be considered an uppercase password.
Just like passwords containing only lowercase letters, uppercase-only passwords are generally less secure than those that use a mix of character types. This is because limiting a password to uppercase letters only reduces the number of possible character combinations, making the password more vulnerable to brute-force attacks, where every possible combination is tried to guess the password.
Here are a few examples of uppercase passwords:
- ROBBIE
- JULIANDOUGLAS
- TAYLORBRANDON
- SAMUELSTEWART
What is a Lowercase and Uppercase Password Example?
An uppercase or lowercase letter in a password is simply a letter written in an upper or lowercase form. For example, the letter “a” can be written in both uppercase (A) and lowercase (a).
As mentioned, many websites require using lowercase and uppercase letters when creating a password. These passwords are a combination of both lowercase and uppercase letters.
By using a combination of both lowercase and uppercase letters, you can make your password more secure. For example, “jacktyler” or “JACKTYLER” are considered weak passwords.
Because many people use their name or the name of a loved one as their password, hackers can easily guess these passwords.
But if you mix up both lowercase and uppercase letters, such as “JaCkTylEr” or “jAcKtYlEr”, you can make your password much more secure and difficult to guess.
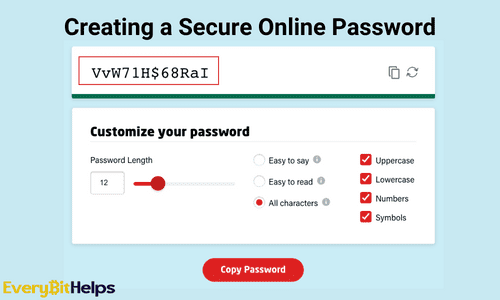
Here are some examples of passwords that use both lowercase and uppercase letters:
- JaCkTylEr
- gReenbOaRd
- bLuEfLoWeR
- aPplEsHAde
- JustinBeiber
As you can see, using lowercase and uppercase letters makes it much more difficult for hackers to guess your password. So, use lowercase and uppercase letters when creating a strong password.
What are 6-Character Password Examples?
Passwords that consist of 6 characters are considered 6-character passwords.
Here are some examples of 6-character passwords:
- Beaver
- RaisiN
- ReDliP
- Greens
What are 8-Character Passwords?
8-character passwords are passwords that consist of 8 characters with both lowercase and uppercase letters. These passwords are considered more secure than shorter ones and are recommended by many security experts and websites.
Some websites will require you to use long passwords that usually require you to use at least 8 characters. However, you can always add more characters to make your passwords even more secure.
Here are some examples of 8-character passwords:
- fErnGrEy
- RiVefLow
- steVAnPaul
- HarryPotter
What is a Special Character Password?
Passwords with special characters contain special characters such as symbols and punctuation marks (#, $, %, @, !, &, *).
Here are some examples of passwords with special characters:
- johN&SmitH
- Molly!FooBar
- blUe$StaR%
- Go*fLov3r

How to Create a Strong Password?
A robust password is a barrier against unauthorized access, safeguarding our personal, financial, and professional information from potential threats and cyberattacks. The strength of your password directly impacts your online safety. Investing a little time in creating a robust password can save you from potential cyber headaches in the future.
Weak or easily guessable passwords are akin to unlocking your front door, inviting cybercriminals to exploit your data. This can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and unauthorized use of sensitive information.
Here’s how to fortify your online defences with a strong password:
- Length Matters: Aim for a password between 8-64 characters. The longer it is, the harder it becomes to crack.
- Diverse Characters: Use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters. This variability makes it more challenging for hackers to predict.
- Numbers and Symbols: Incorporate at least one number and one special character. These add layers of complexity.
- Avoid the Obvious: Refrain from using easily decipherable information like your pet’s name, birthdays, or sequential numbers.
- Consider Tools: Think about using a password manager. It stores your passwords securely and can generate strong, random passwords.
Examples of a Strong Password
A robust password relies on its length and diverse character by using a combination of words, numbers and symbols that strike a balance between complexity and memorability.
Below are some examples of strong passwords:
Qw4!zGp9&yT*mN8#rLx2@oV3tB6^jEw0%zK7Hs3!pU8&dQ5*fG7#oLz4^iX1
Remember, these are just examples. When creating your own strong password:
- Randomness is Key: Avoid using easily guessable patterns or sequences.
- Mix Different Character Types: Use a combination of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid Personal Information: Refrain from using easily accessible information like birthdays, anniversaries, or names of family members.
- Length: The longer the password, the better. Aim for at least 12 characters if possible.
If you decide to use or are inspired by the above examples, ensure you modify them to suit your needs and avoid using them as they are.
How to Avoid Weak Passwords
It’s important to sidestep typical password pitfalls that cybercriminals often exploit. Given the ubiquity of social media, personal details are now more accessible, making them prime targets for hackers.
Below are some typical password missteps to avoid:
- Obvious Choices: Avoid using “password” as your password.
- Simple Sequences: Steer clear of easily guessable patterns like “12345678.”
- Personal Details: Refrain from incorporating readily available information such as birthdates, family names, addresses, or names of pets and children.
By being mindful of these common vulnerabilities, you can significantly enhance your digital security.
Password Alternatives
As the digital landscape evolves, so do methods of ensuring user online security. Passwordless authentication simplifies the login process, particularly for mobile and social platform users. Instead of remembering a password, users get a one-time code through text, email, or other messaging services for instant login.
Below are some advanced authentication alternatives. These methods offer convenience and enhanced security, adapting to users’ needs.
- Two-factor Authentication (2FA): Combines two verification methods, often something the user knows (e.g., password) and something they possess (e.g., smartphone).
- Multifactor Authentication (MFA): An enhanced version of 2FA, it uses multiple verification methods, not limited to just two.
- Biometrics: Uses unique physical (e.g., fingerprint) or behavioural (e.g., voice pattern) traits for authentication.
- Tokens: Physical devices, like key fobs or smart cards, are carried by users to grant access.
- One-Time Passwords (OTP): Automatically generated passwords for a single use, often stored on security tokens.
- Social Login: Allows users to log in using their social media accounts, eliminating the need for separate site-specific credentials.
What is a Password Manager?
A password manager is a software application that helps users create and store passwords for various websites and applications. Its purpose is to make it easier for users to remember and keep track of their passwords while preventing them from having to remember hundreds (or even thousands) of individual passwords.
Why Use A Password Manager?
Password managers can save users time and hassle by making it easy to create and store passwords for various sites and applications. A password manager can also help protect users from password theft, as it automatically generates new passwords whenever their current password expires. A password manager can also help users keep track of their online security settings by storing passwords in one place.
LastPass Password Manger
LastPass is a well-known password manager where you can securely save your usernames and passwords. If you use too many online accounts and different usernames and passwords for each one, you can easily forget and lose track of them.
But with LastPass, you can store all these accounts and passwords in one place and access them with a single master password. This makes managing your online accounts and passwords easy and keeps them secure from hackers.
Here are some of the key features of LastPass:
- Password Manager: You can store all your usernames and passwords in one place so you don’t have to remember them.
- Passwords Vault: All your passwords are stored in a secure vault, so no one else can access them but you.
- Save & Autofill: One of the most valuable features of LastPass is that it can save and autofill your usernames and passwords when you visit a site. So when you visit a website, LastPass will automatically fill in your username and password.
- Password Generator: Can’t find the right password? LastPass can generate a secure and random password for you.
- Password Sharing: Using the LastPass password-sharing feature, you can securely share passwords with other users.
- Dark Web Monitoring: LastPass can monitor the dark web to see if your credentials are being sold or traded. If any of your info is found, LastPass will alert you immediately.
- Security Dashboard: LastPass offers a security dashboard where you can see your saved passwords and ensure they are secure. You can make changes or update any of your passwords if needed.
How Does LastPass Work?
LastPass works as an extension to your web browser. First, you must create your LastPass account and connect it to your browser. Then, you can save all your usernames and passwords in the LastPass Vault.
When you visit a website requiring login credentials, LastPass will automatically fill in the form.
It’s important to remember that your master password is the only one that unlocks your LastPass vault, so make sure you choose a strong master password.

Conclusion
So there you have it! Now you know everything there is to know about lowercase & uppercase passwords. The internet is full of scammers and hackers looking for easy targets to steal sensitive data.
But if you use strong passwords with lowercase & uppercase letters and special characters, you can protect your data from these malicious attackers. Use tools like LastPass to keep track of your passwords and ensure their safety.
Remember to always stay vigilant with your online security and never share your credentials with anyone!
FAQs
Can a strong password be hacked?
Yes, a strong password can be hacked. However, a password manager can help protect users from remembering a strong password whenever they log in to a site or application. A password manager can also help users create complex passwords that are more difficult to hack.
What is the meaning of uppercase in a password?
Uppercase in a password refers to the use of capital letters, which are the larger and more prominent versions of the standard, smaller, lowercase letters. Using uppercase letters in a password adds complexity and increases the security of the password. This is because it makes it more difficult for hackers to guess or crack passwords through brute force attacks or other methods.
How often should passwords be changed?
It’s recommended to update your password every three to six months. When choosing a new one, make sure it’s different from previous passwords. Advanced password generation tools also ensure that the new passwords significantly differ from the ones previously used.